If you use GitHub action workflows that run over and over again (either manually, event based or scheduled), it is sometimes helpful to compare the last return state with the current one to detect changes. In this article I show you one way how to do that.
The basic GitHub workflow
The below GitHub workflow (defined in the file .github/workflows/workflow_history.yaml will be the starting point with two steps:
- It checks out the repository (this is important to determine the status later)
-
On manual invocation, it displays a checkbox named "Fail the job?". If this is checked, the job will fail, otherwise it will pass.
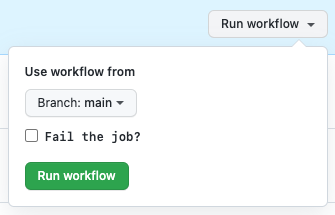
Github action invocation
---
name: 'Github Workflow History'
'on':
workflow_dispatch:
inputs:
failJob:
description: Fail the job?
type: boolean
required: true
default: false
jobs:
exampleJob:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Checkout
uses: actions/checkout@v3
- name: Pass or fail job
run: exit 1
if: github.event.inputs.failJob == 'true'For testing purposes, I ran the job twice, once with a successful outcome, once with a failure:
Getting the last job status with the GitHub CLI
List previous runs
GitHub CLI is the official command line tool for Github that can perform various tasks on repositories. One of these is checking a workflow job history - this will come in handy.
To test this approach, I installed the CLI tool locally by following this instruction. In the end, we will use it from inside the workflow, of course.
This is the syntax to determine the last job status by passing the yaml file name:
gh run list --workflow workflow_history.yamlThis returns the following results:
STATUS NAME WORKFLOW BRANCH EVENT ID ELAPSED AGE
X Update workflow_history.yaml Github Workflow History main workflow_dispatch 2481361465 13s 1d
✓ Update workflow_history.yaml Github Workflow History main workflow_dispatch 2481359101 12s 1dGet only the last run
Per default, this lists the job status sorted by date, newest first.
Luckily, we can get only the last one with the --limit option:
gh run list --workflow workflow_history.yaml --limit 1which returns only the latest job status.
X Update workflow_history.yaml Github Workflow History main workflow_dispatch 2481361465 13s 1dGet only the status of the last run
This is great, but we only need the status of the last run, not all the other information.
This is where awk comes in. This linux command line tool cuts a string tab separated string (if no custom separator is specified) and can then be used to retrieve a specific part.
-
awk '{print $1}'would give us the first part of the string from the beginning until the first tab -
awk '{print $2}'would give us the part after the second tab, etc.
Since the gh run list command has the job completion status as the first part of the string (e.g. completed, _inprogress, etc.), we are interested in the second which returns either failure or success:
gh run list --workflow workflow_history.yaml --limit 1 | awk '{print $2}In our case, this returns failure since the latest job invocation returned an error.
Perfect! Or is it?
A small issue
Unfortunately, there is a problem - the status is only there on jobs that are not in_progress like here:
in_progress Update workflow_history.yaml Github Workflow History main workflow_dispatch 2489395313 15s 0m
completed success Update workflow_history.yaml Github Workflow History main workflow_dispatch 2489383728 22s 2m
completed failure Update workflow_history.yaml Github Workflow History main workflow_dispatch 2489367709 32s 4mIn this case, we would get Update since there is no success or failure status for jobs that are still running. So there needs to be a change to our initial CLI command:
gh run list --workflow workflow_history.yaml | grep -oh "completed.*" | head -1 | awk '{print $2}'This command works much better because it will only take the completed jobs into account:
-
gh run list --workflow workflow_history.yamlreturns the list of jobs:in_progress Update workflow_history.yaml Github Workflow History main workflow_dispatch 2489473415 11s 0m completed success Update workflow_history.yaml Github Workflow History main workflow_dispatch 2489395313 23s 14m completed success Update workflow_history.yaml Github Workflow History main workflow_dispatch 2489383728 22s 15m completed success Update workflow_history.yaml Github Workflow History main workflow_dispatch 2489373971 29s 17m completed failure Update workflow_history.yaml Github Workflow History main workflow_dispatch 2489367709 32s 18m completed success Update workflow_history.yaml Github Workflow History main workflow_dispatch 2489358495 38s 20m completed failure Update workflow_history.yaml Github Workflow History main workflow_dispatch 2481361465 13s 1d completed success Update workflow_history.yaml Github Workflow History main workflow_dispatch 2481359101 12s 1d - By piping this to
grep -oh "completed.*", we filters out all incomplete jobs, leavingcompleted success Update workflow_history.yaml Github Workflow History main workflow_dispatch 2489395313 23s 14m completed success Update workflow_history.yaml Github Workflow History main workflow_dispatch 2489383728 22s 15m completed success Update workflow_history.yaml Github Workflow History main workflow_dispatch 2489373971 29s 17m completed failure Update workflow_history.yaml Github Workflow History main workflow_dispatch 2489367709 32s 18m completed success Update workflow_history.yaml Github Workflow History main workflow_dispatch 2489358495 38s 20m completed failure Update workflow_history.yaml Github Workflow History main workflow_dispatch 2481361465 13s 1d completed success Update workflow_history.yaml Github Workflow History main workflow_dispatch 2481359101 12s 1d - With
head -1we only keep the top line (which is the newest run):completed success Update workflow_history.yaml Github Workflow History main workflow_dispatch 2489395313 23s 14m - Finally, we can retrieve the status with
awk '{print $2}'as before:success
Calling GitHub CLI from the runner
Since the GitHub runners that are in charge of executing workflows have the GitHub CLI built in, we can perform this operation also from our yaml file:
- name: Check last job status
id: lastJobStatus
if: always()
run: |
LAST_JOB_STATUS=$(gh run list --workflow workflow_history.yaml | grep -oh "completed.*" | head -1 | awk '{print $2}')
THIS_JOB_STATUS="${{ job.status }}"
env:
GITHUB_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}There are some important parts to this:
- We specify the
id: lastJobStatussince we want to have access to the status of the last job from subsequent steps. Without an id, we cannot access any variables this job sets later on in the process. -
if: always()means that this step will always be executed, regardless of the status of the previous one. Without this, it would be skipped if the previous step fails. - The line
LAST_JOB_STATUS=$(gh run list --workflow workflow_history.yaml | grep -oh "completed.*" | head -1 | awk '{print $2}')calls the shell command we tested above and saves its result in a new variable calledLAST_COMPLETED_JOB_STATUS. - The job status of the current run can be retrieved with GitHub's
${{ job.status }}variable. This we save inTHIS_JOB_STATUSfor readability. - In the
env:block, we need the lineGITHUB_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}. It stores the GitHub token of this repository in the environment variableGITHUB_TOKENwhich is required for GitHub CLI to work properly. This token is automatically regenerated for every workflow run by GitHub.
Now we should have the current and the last job status.
Detecting the changed job run status
Now we are missing some logic to check if the status was actually changed. We can modify the script from above to include this:
run: |
LAST_JOB_STATUS=$(gh run list --workflow workflow_history.yaml | grep -oh "completed.*" | head -1 | awk '{print $2}')
THIS_JOB_STATUS="${{ job.status }}"
if [ "$LAST_JOB_STATUS" != "$THIS_JOB_STATUS" ]; then
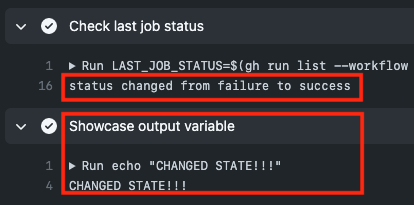
echo "status changed from $LAST_JOB_STATUS to $THIS_JOB_STATUS"
echo "::set-output name=changedState::true"
else
echo "status is still $THIS_JOB_STATUS"
echo "::set-output name=changedState::false"
fiHere we added an if condition that compares the $LAST_JOB_STATUS to the $THIS_JOB_STATUS variable. If both are different, we know that the status changed. Otherwise, the status is still like the former run.
To debug this, we echo out the result of this check (either status changed from $LAST_JOB_STATUS to $THIS_JOB_STATUS or status is still $THIS_JOB_STATUS).
Additionally, we use GitHub's mechanism to set step output variables using echo "::set-output name=changedState::true" or echo "::set-output name=changedState::false". This way, subsequent steps can check this and know if we have a changed status.
Subsequent steps
Finally, let's add one step afterwards that is executed only if we have a changed state. This uses the output variable from above as a condition.
- name: Showcase output variable
if: always() && steps.lastJobStatus.outputs.changedState == 'true'
run: echo "CHANGED STATE!!!"Here, we use the always() && steps.lastJobStatus.outputs.changedState == 'true' to execute this step when our custom variable from above is set to true (lastJobStatus is the id of the step that set the output variable before).
Result
If we have a changed state like this
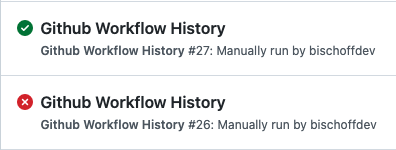
we see the correct result and that the step is properly executed:
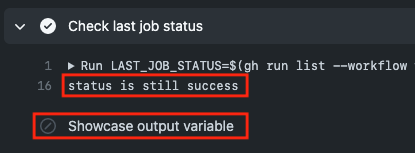
In case the former state is the same
we see this:
This is it!
Complete workflow
This is the complete workflow script:
---
name: 'Github Workflow History'
'on':
workflow_dispatch:
inputs:
failJob:
description: Fail the job?
type: boolean
required: true
default: false
jobs:
exampleJob:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Checkout
uses: actions/checkout@v3
- name: Pass or fail job
run: exit 1
if: github.event.inputs.failJob == 'true'
- name: Check last job status
id: lastJobStatus
if: always()
run: |
LAST_JOB_STATUS=$(gh run list --workflow workflow_history.yaml | grep -oh "completed.*" | head -1 | awk '{print $2}')
THIS_JOB_STATUS="${{ job.status }}"
if [ "$LAST_JOB_STATUS" != "$THIS_JOB_STATUS" ]; then
echo "status changed from $LAST_JOB_STATUS to $THIS_JOB_STATUS"
echo "::set-output name=changedState::true"
echo "::set-output name=stateMessage::Test status changed from '$LAST_COMPLETED_JOB_STATUS' to '$THIS_JOB_STATUS'."
else
echo "status is still $THIS_JOB_STATUS"
echo "::set-output name=changedState::false"
echo "::set-output name=stateMessage::$THIS_JOB_STATUS"
fi
env:
GITHUB_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
- name: Showcase output variable
if: always() && steps.lastJobStatus.outputs.changedState == 'true'
run: echo "CHANGED STATE!!!"